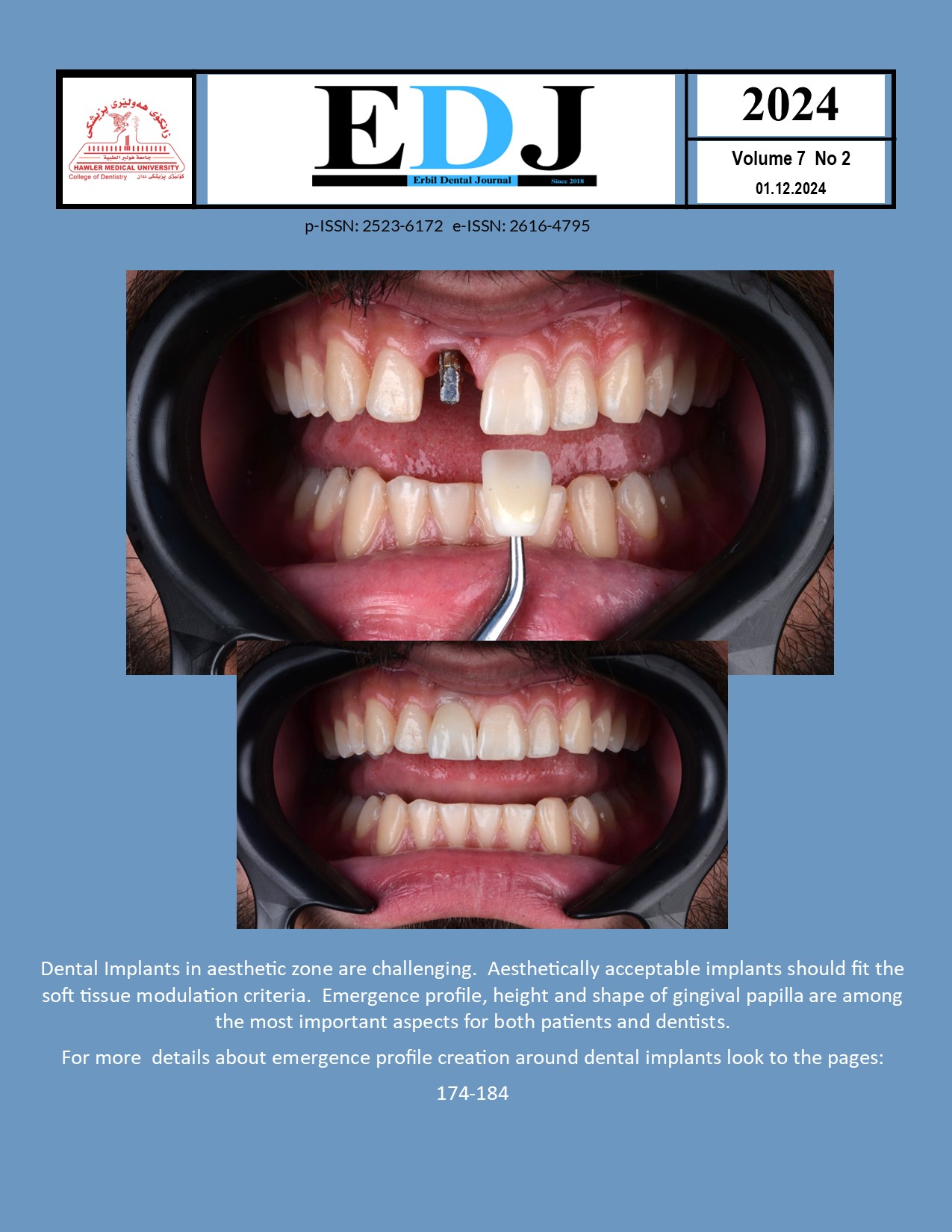
Optimizing Soft Tissue Emergence Profile Around One-Piece Dental Implants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15218/edj.2024.19Keywords:
Aesthetic Zone, Clinical Studies/Trials, Cervico System, Customized Healing Abutment, One-piece Dental implantsAbstract
Background and Objective: One-piece implants were introduced many years ago, however, in the last years, they have gained acceptance as a therapeutic alternative for many clinical cases. The soft tissue surrounding the neck of one-piece implants, particularly in the esthetic zone, is a cause for concern despite the clinical effectiveness of these implants. The purpose of this study is to propose a simple way for optimizing soft tissue around one-piece dental implants.
Material and Methods: Between January 2022 and January 2024, a total of 137 patients were treated with single-piece dental implants that were placed in the aesthetic anterior region of the mouth. A temporary crown in the office was created using a flowable composite that was temporary in nature using the mold of the Cervico system (VP Innovato Holdings Ltd, Lemessos, Cyprus). After three months, the patients' rates of success, failure, and complications were evaluated. The Jemt Papillary Index was employed to assess the papilla following the placement of the final prosthesis, a Satisfaction Visual Analog Scale (VAS system) was created to gauge the patient's satisfaction. The data was evaluated by means of descriptive statistics utilizing the SPSS (version 30) package of software.
Results: The mean age of all cases was 32.10 years, with 78 (56.9%) male cases and 59 (43.1%) female cases. After 3 months among 137 inserted implants; 97.8% of the implants were successfully osseointegrated. After removal of the temporary crown a very nice anatomical emergence profile created and the results of papilla index after three months showed that the majority of the cases (84 cases comprises 61.3%) ended with score number 3, which means Optimal soft tissue contour and the papillae fill up the entire proximal space. Finaly the results of Satisfaction Visual Analog Scale (VAS) showed that 120 cases (87.6%) were have most positive response to the dental implant treatment.
Conclusion and Clinical implications: We concluded that using of a customized composite temporary crown fabricated by Cervico system offers a very simple and time-saving technique for the clinician, aiding in splinting the implants and obtaining nice emergence profile around one-piece implants.
References
Schoenbaum, T.R., Alawie. Emergence Profile of the Implant Abutment and Its Effects on the Peri-implant Tissues. In: Schoenbaum, T. (eds) Implants in the Aesthetic Zone. Springer, Cham; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72601-4_11.
Zembić A, Johannesen LH, Schou S, et al. Immediately restored one-piece single-tooth implants with reduced diameter: one-year results of a multi-center study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(1):49-54.
Quirynen M, Van Steenberghe D. Bacterial colonization of the internal part of two-stage implants. An in vivo study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1993;4(3):158-161.
Jervøe-Storm PM, Jepsen S, Jöhren P, et al. Internal bacterial colonization of implants: association with peri-implant bone loss. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(8):957-963.
Jones AA, Cochran DL. Consequences of implant design. Dent Clin North Am. 2006;50:339–360.
Ali, S., Mahmud, P., Othman, K. and Samad, A. (2019) Single Piece Dental Implant: A Remedy for Atrophic Ridges: Review. International Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 8, 271-282. doi: 10.4236/ijohns.2019.86025.
Prithviraj DR, Gupta V, Muley N, Sandhu P. One-piece implants: Placement timing, surgical technique, loading protocol, and marginal bone loss. J Prosthodont 2013;22:237-44.
Srivastava, Sumedha; Kalburgi, Veena; Banerjee, Nilojjawala; Tripathi, Bimmi; Jain, Milan1; Singh, Shivam2. Biological Width around One- and Two-piece Implants: A Systematic Review. Journal of Head & Neck Physicians and Surgeons 12(1):p 28-37, Jan–Jun 2024. | DOI: 10.4103/jhnps.jhnps_45_24.
Vergoullis I, Badell C, Papadopoulos G. An Innovative Approach for the Selection, Generation and Recording of a Custom Emergence Profile Around Implants. Journal of Implants and Advanced Clinical Dentistry. July 2017: Vol (9). No5: 6-19.
Jemt T. Regeneration of gingival papillae after single implant treatment. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1997; 17:326–333.
Jivraj S, Chee W, Corrado P. Treatment planning of implants in the aesthetic zone. Br Dent J. 2006;201(2):77-89.
Cosyn J, De Bruyn H. Guidelines for the design of implant-supported single crowns and fixed partial dentures. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40(10):1052-1060.
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Polyzos IP, et al. Timing of implant placement after tooth extraction: immediate, immediate-delayed or delayed implants? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010;3(3):189-205.
Jawad M. Mikaeel. One Piece Dental Implants in Esthetic Zone. Sulaimani Dent J. 2021;8(1):7. doi:10.17656/sdj.10128.
J. Barrachina-Diez, E. Tashkandi, S. Stampf and W. Att. Long-Term Outcome of One-Piece Implants. Part I: Implant Characteristics and Loading Protocols. A Systematic Literature Review with Meta-Analysis. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants 2013 Vol. 28 Pages 503-18. DOI: 10.11607/jomi.2790
Chen ST, Buser D. Esthetic outcomes following immediate and early implant placement in the anterior maxilla—a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(Suppl):186-215.
Lang NP, Pjetursson BE, Tan K, et al. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of fixed partial dentures (FPDs) after an observation period of at least 5 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15(6):625-642.
Tarnow DP, Chu SJ, Salama MA, et al. Flapless postextraction socket implant placement in the esthetic zone: Part 1. The effect on bone and soft tissue healing in a canine model. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013;33(2):177-185.
Linkevicius T, Apse P, Grybauskas S, et al. Influence of micro-gap location and configuration on peri-implant tissues: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(2):266-276.
Belser UC, Grütter L, Vailati F, et al. Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single-tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: a cross-sectional, retrospective study in 45 patients with a 2- to 4-year follow-up using pink and white esthetic scores. J Periodontol. 2009;80(1):140-151.
Schwarz F, Mihatovic I, Golubovic V, et al. Impact of implant-abutment connection and placement depth on crestal bone level changes: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(4):417-425.
Thoma DS, Brägger U, Hämmerle CH, et al. A systematic review of soft tissue alterations and esthetic outcomes following immediate implant placement and restoration. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41(10):505-515.
Kois JC. Predictable single-tooth peri-implant esthetics: five diagnostic keys. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2001;22(3):199-206.
Lindhe J, Meyle J. Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35(8 Suppl):282-285.
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Abduljaleel Azad Samad (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The copyright on any article published in Erbil Dental Journal is retained by the author(s) in agreement with the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike License (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).